En
Considering solar for your home or business? You’re probably wondering which type of solar system fits your needs. Grid-tied, off-grid, and hybrid systems each have their own vibe, costs, and benefits. Whether you’re looking to slash utility bills, live off the land, or have a backup plan for outages, this guide breaks down the three main solar system types in plain English. We’ll cover how they work, who they’re for, and what you need to know to pick the right one for your setup, with insights to help you make a smart choice.
Solar systems come in three main flavors: grid-tied, off-grid, and hybrid. Each connects to the power grid (or doesn’t) in a different way, affecting how you use, store, or sell solar energy. Grid-tied systems stay connected to the utility grid, off-grid systems are fully independent, and hybrid systems blend the best of both worlds with backup storage. Let’s dive into each type to see what makes them tick.
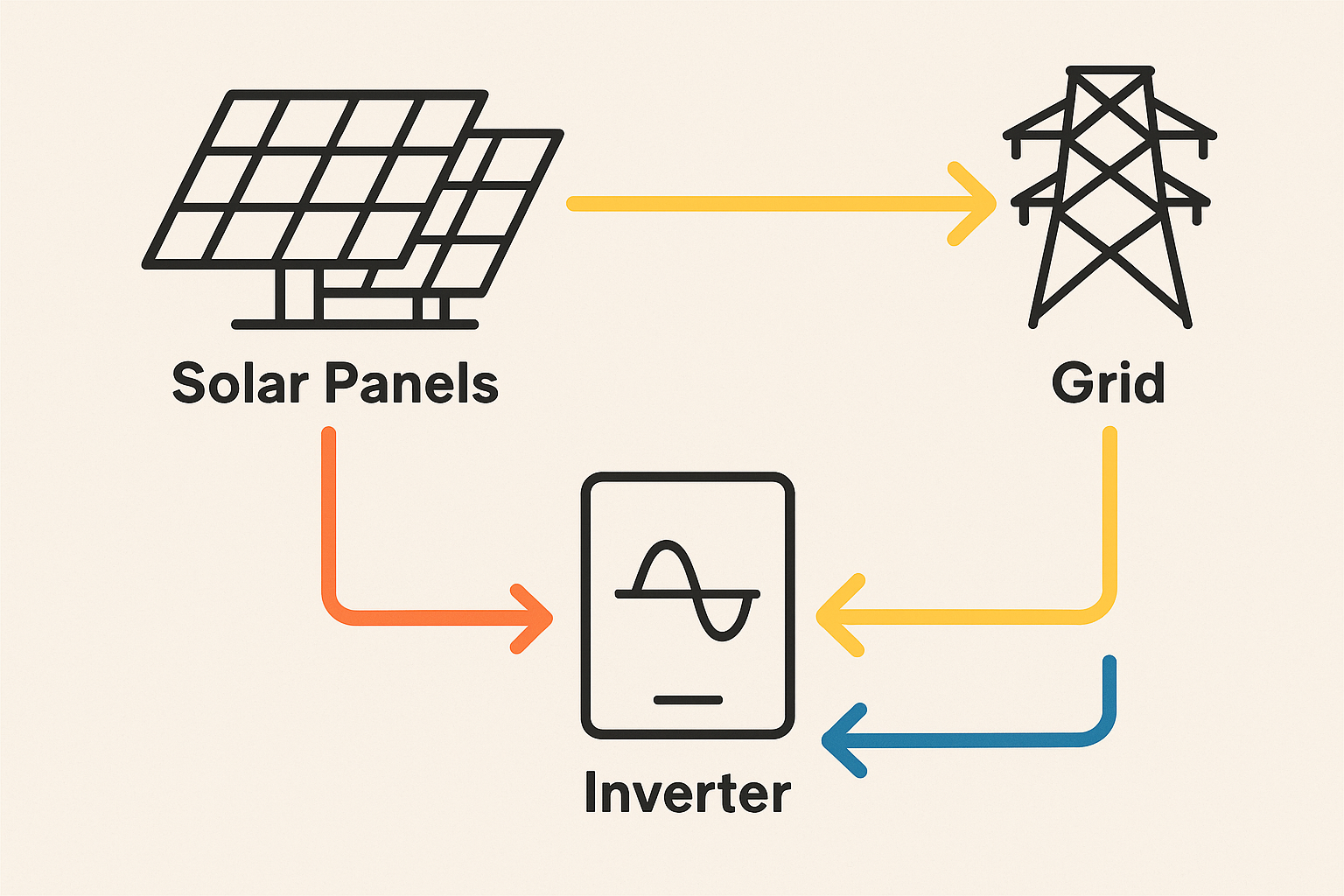
Grid-tied inverter systems are the most common, especially for homes and businesses in urban areas. They use solar panels to generate electricity, which is converted from DC to AC by an inverter for your use. Excess power flows back to the grid, often earning you credits through net metering. When your panels aren’t producing (like at night), you pull power from the grid. No batteries needed, which keeps things simple and affordable.
Insight: Grid-tied systems are a no-brainer for businesses with high daytime energy use, like offices or retail stores, since they maximize savings through net metering in regions with supportive policies.
Pros | Cons |
Lower upfront costs (no batteries) | No power during grid outages |
Net metering can reduce bills | Dependent on grid reliability |
Simple installation and maintenance | Less control over energy source |
Ideal for urban or suburban settings | Savings vary by utility rates |
Insight: If your area has frequent outages, a grid-tied system might leave you in the dark unless you add a small backup battery for critical loads.
Off-grid inverter systems are the rebels of the solar world, operating without any grid connection. They rely on solar panels, a robust battery bank, a charge controller, and an inverter to provide power 24/7. You generate and store all your electricity, making them perfect for remote locations like rural homes, cabins, or off-grid businesses (think farms or eco-resorts).
Pros | Cons |
Complete energy independence | Higher upfront costs (batteries) |
No utility bills | Requires careful energy management |
Ideal for remote or rural areas | Larger system size for year-round use |
Eco-friendly, zero-grid reliance | Maintenance for batteries |
Insight: Off-grid systems shine for businesses like agritourism ventures, where showcasing sustainability can attract customers, but you’ll need to size the system carefully to handle peak loads.
Hybrid solar inverter systems are the Swiss Army knife of solar setups They’re grid-tied for efficiency but include battery storage for backup during outages or to store excess solar energy. You can use stored power at night, during peak rate hours, or when the grid goes down. Advanced inverters and energy management systems let you optimize when to use solar, battery, or grid power.
Insight: Hybrid systems are gaining traction for commercial properties like warehouses, where battery backup can power critical systems like refrigeration during outages, saving thousands in losses.
Pros | Cons |
Backup power during outages | Higher costs than grid-tied systems |
Flexibility to use grid or batteries | Complex installation and maintenance |
Optimizes savings with time-of-use | Batteries need replacement over time |
Great for areas with unreliable grids | Requires space for battery storage |
Picking the right system depends on your location, energy needs, budget, and goals. Here’s a quick guide:
System Type | Best For | Key Consideration |
Grid-Tied | Urban businesses, homes with reliable grids | Net metering policies and electricity rates |
Off-Grid | Remote homes, farms, or eco-focused businesses | Battery sizing and year-round sunlight |
Hybrid | Businesses or homes with outages or high peak rates | Balancing upfront costs with backup needs |
· Energy Usage: Analyze your electricity bills to size the system. A 10 kW system might suit a small business, while a 50 kW system could power a larger facility.
· Location: Urban areas favor grid-tied or hybrid systems; rural spots lean toward off-grid.
· Budget: Grid-tied is cheapest upfront, while off-grid and hybrid require battery investments.
· Incentives: Check for tax credits (e.g., 26% ITC in the U.S.) or local rebates to offset costs.
Insight: Businesses with time-of-use (TOU) rates can save big with hybrid systems by storing solar energy during low-rate periods and using it when rates peak.
Solar tech is evolving fast, and here are some trends to watch in 2025:
· Smart Energy Management: Hybrid systems now integrate with AI-driven software to optimize energy use based on weather, grid rates, and demand.
· Advanced Batteries: Lithium-iron-phosphate (lithium LiFePO4) batteries are becoming standard for off-grid and hybrid systems, offering longer lifespans and safety.
· Bifacial Panels: These capture sunlight on both sides, boosting efficiency for grid-tied and hybrid systems, especially in reflective environments like snowy regions.
· Solar-Plus-EV: Businesses are pairing solar with EV charging stations, appealing to eco-conscious customers and employees.
Insight: Investing in a hybrid system with smart energy management can future-proof your business against rising utility rates and grid instability.
How much does an off-grid solar system cost for a remote cabin?
A 5–10 kW off-grid system with batteries costs $15,000–$40,000, depending on location, battery size, and panel efficiency. Rural areas with good sunlight reduce costs.
Can a hybrid solar system save money on time-of-use rates?
Yes, hybrids store solar energy during low-rate periods and use it during peak hours, cutting bills by 20–40% in TOU regions.
What size solar system do I need for an off-grid home?
A typical off-grid home needs 5–15 kW, depending on appliances and usage. An energy audit can pinpoint your needs—ask Raisun Power for a free consultation.
Are there tax incentives for hybrid solar systems in 2025?
Yes, the U.S. ITC (26%) applies to hybrid systems, including batteries. State-specific rebates may also be available—check with your local utility.
How long do batteries last in off-grid or hybrid solar systems?
Lithium batteries last 10–15 years, with warranties typically covering 70% capacity after 10 years. Regular maintenance extends lifespan.
Ready to find the perfect solar system for your home or business? Raisun Power offers customized grid-tied, off-grid, and hybrid solutions to fit your needs. Reach out today for a free quote and start powering your future with solar!